
Our guide QuickBooks will navigate through this essential managerial accounting tool, breaking down complex terms and components into digestible morsels. We’ll illustrate how demystifying COGM can streamline your inventory management and hone your production efficiency. Real-time data syncingSynder automatically syncs your financial data—sales, fees, refunds, and more—as transactions happen.

Manufacturing Accounting: Strategies for Success
11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site. All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own.
Aids in Finding Financial Losses
- Manufacturing costs from previous periods tie into current accounts through this opening WIP number.
- In spite of the similarities in the names, the cost of goods manufactured (COGM) is not interchangeable with the cost of goods sold (COGS).
- The main difference lies in whether the goods are sitting in inventory (COGM) or have been purchased by customers (COGS).
- With built-in formulas and fields, a COGM calculator template facilitates quick data entry and instantaneous results.
- COGM establishes the overall cost of converting raw materials into marketable finished items.
- At the beginning of the year, XYZ Inc. had $50,000 worth of work-in-progress inventory.
This cost is easily traceable to the end product as cogm formula it is directly related to the production process, and you can not separate this from it. In order to determine the actual direct materials used by the company for production, we must consider the Raw Materials Inventory T-account. Raw materials inventory refers to the inventory of materials that are waiting to be used in production.
Difference between Cost of Goods Manufactured and Total Manufacturing Cost
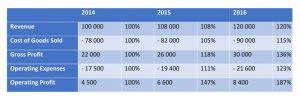
The (COGS) is an essential component that provides a clear picture to business owners and managers about the company’s manufacturing performance. Only after the cost of goods manufactured is calculated can a company compute its cost of goods sold. To calculate direct labor, you have to calculate the direct hourly labor rate and the direct labor hours. The sum of those three costs, i.e. the manufacturing costs, is $50 million. COGM is assigned to units in production and is inclusive of WIP and finished goods not yet sold, whereas COGS is only recognized when the inventory in question is actually sold to a customer.
How can Synder simplify accounting?

Calculating COGM means adding up all the direct and indirect costs involved in making products, plus accounting for changes in work-in-process (WIP) inventory. To figure out COGM, you need to know the total manufacturing costs (TMC) and the WIP inventory values at the start and end of the period. Direct labor refers to an organization’s labor cost Airbnb Accounting and Bookkeeping in preparing, assembling, and manufacturing its goods with raw materials. Prime cost is the total manufacturing cost excluding the value of direct materials.

Can You Explain the Difference Between COGM and COGS?
A high rate indicates that the company’s manufacturing operations may not be utilizing the resources available as efficiently as they should. On the other hand, a low rate points towards effective and efficient resource use. Every business owner must know and understand every aspect of their company, including the key metrics that help determine how well the business is fairing. John Manufacturing Company, a manufacturer of soda bottles, had the following inventory balances at the beginning and end of 2018.
- The cost of goods manufactured is included in a company’s income statement, usually together with the beginning and ending finished goods inventories.
- Most manufacturers strive toward minimizing the ending WIP as it frees up capital, deflates the tax burden, and crucially, makes accounting much easier.
- You can reduce the expense of raw materials by buying them at a lower price.
- My Accounting Course is a world-class educational resource developed by experts to simplify accounting, finance, & investment analysis topics, so students and professionals can learn and propel their careers.
- Management can evaluate each component of the COGM formula when it is fully aware of what a company is generating.
- You can reduce the number of raw materials you use in manufacturing your products without reducing or compromising their quality.
- Take the total manufacturing costs and then subtract the value of the end-of-period WIP inventory.
Advanced COGM Concepts for Seasoned Manufacturers
The COGM of $30,000 represents the total cost of goods completed and ready to sell during the period. This is key for calculating your cost of goods sold (COGS) and analyzing your production efficiency. Work-in-process (WIP) inventory is a big piece of the cost of goods manufactured (COGM) puzzle. Listed as a current asset on the balance sheet, WIP represents the cost of products still in production, including materials, labor, and overhead. With the use of a permanent inventory system for the manufacturing sector, such as an MRP system, businesses may keep track of their production costs and automatically generate numerous KPIs, such as the COGM.
In summary, COGM links to COGS because COGS is the sum of COGM and the change in finished goods inventory during a given period. Use this information to evaluate the cost and profitability of producing and selling a product and make cost management and resource allocation decisions. COGM represents the total cost of the products that have been manufactured and are ready for sale, excluding the cost of finished goods that are still in inventory. Conversely, COGS represents the cost of the products sold to customers during a given period.

 English
English