Adjusting entries update previously recorded journal entries, so that revenue and expenses are recognized at the time they occur. The life of a business is divided into accounting periods, which is the time frame (usually a fiscal year) for which a business chooses to prepare its financial statements. Therefore, it is necessary to find out the transactions relating to the current accounting period that have not been recorded so far or which have been entered but incompletely or incorrectly.
Composition of an Adjusting Entry
For tax purposes, your tax preparer might fully expense the purchase of a fixed asset when you purchase it. However, for management purposes, you don’t fully use the asset at the time of purchase. Instead, it is used up over time, and this use is recorded as a depreciation expense. Whereas you’d record a depreciation entry for a tangible asset, amortization is used to stretch the expense of intangible assets over a period of time.
Introduction to adjusting entries Purpose, types, and composition
- Adjusting journal entries are accounting journal entries that update the accounts at the end of an accounting period.
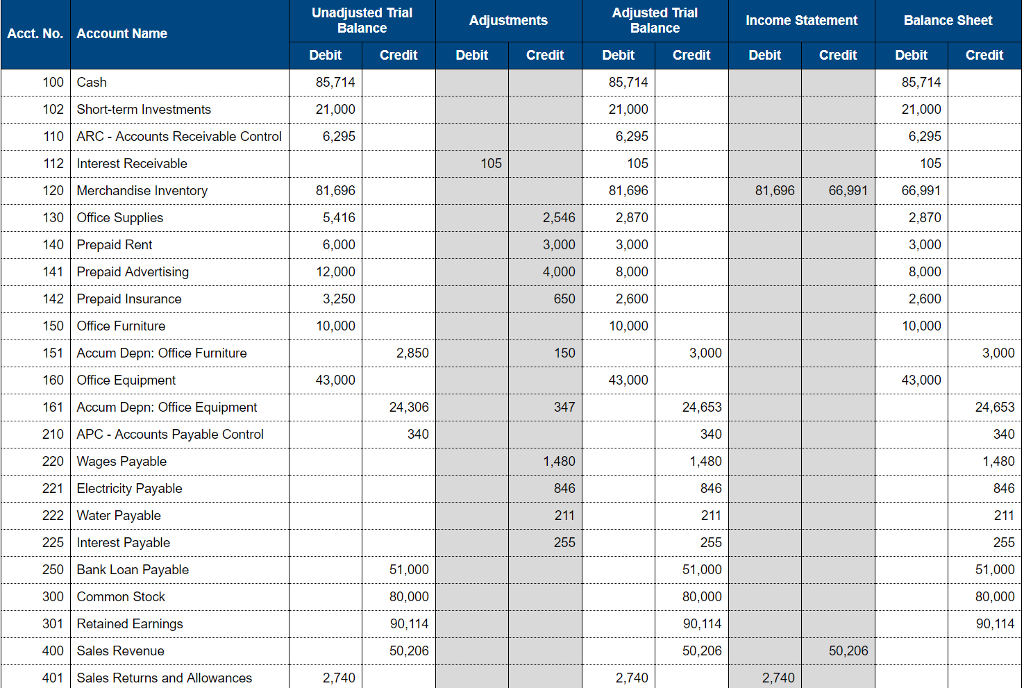
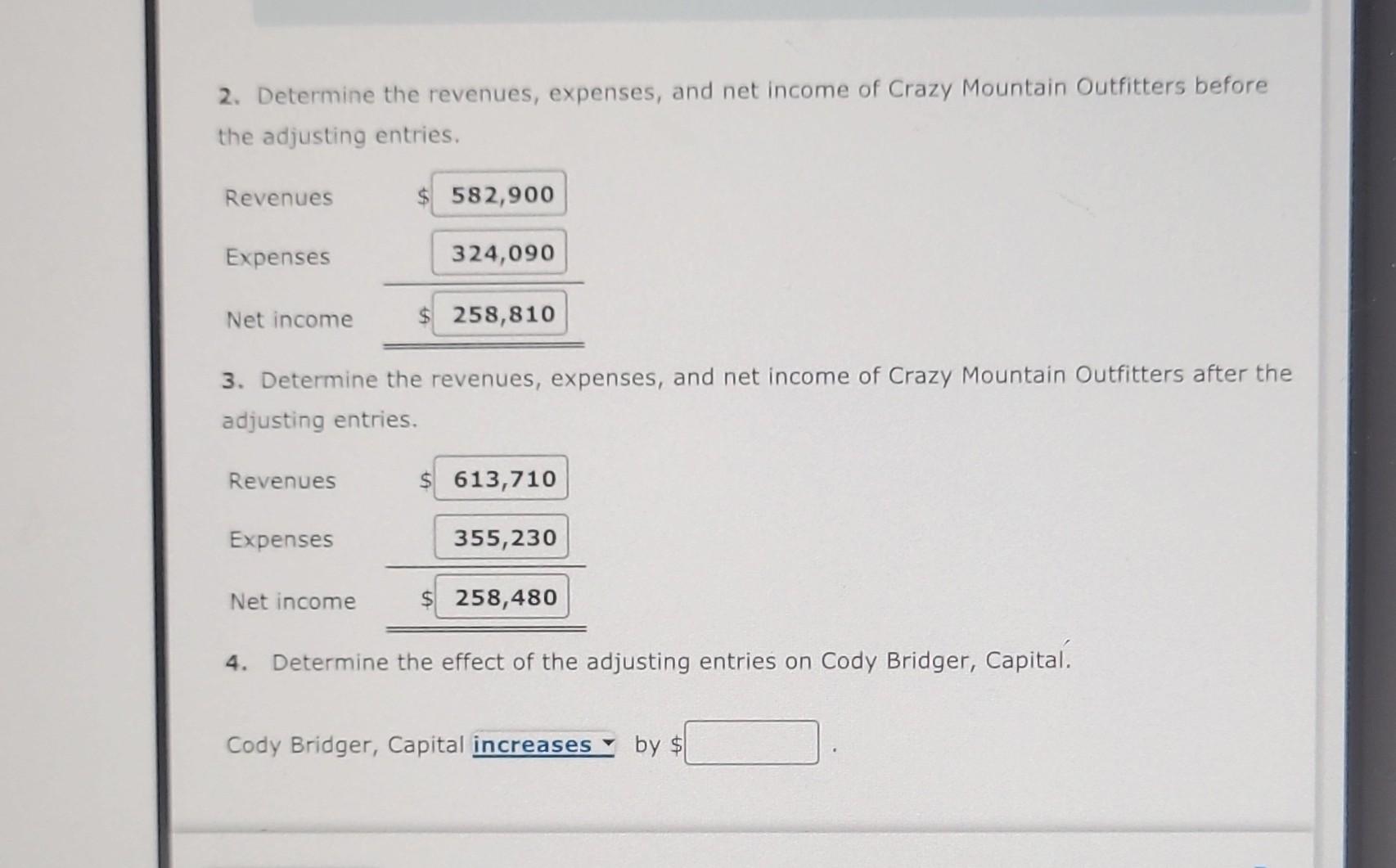
- The following are the updated ledgerbalances after posting the adjusting entry.
- Here are descriptions of each type, plus example scenarios and how to make the entries.
- The primary objective of accounting is to provide information that will help management take better decisions and plan for the future.
The company doesnot use all six months of insurance immediately but over the courseof the six months. At the end of each month, the company needs torecord the amount of insurance expired during that month. Supplies increases (debit) for $400, and Cash decreases (credit)for $400.
What are Adjustment Entries: An Overview
It also helps users (lenders, employees and other stakeholders) to assess a business’s financial performance, financial position and ability to generate future Cash Flows. According to the matching concept, the revenue of the current year must be matched against all the expenses of the current year that were incurred to produce the revenue. If making adjusting entries is beginning to sound intimidating, don’t worry—there are only five types of adjusting entries, and the differences between them are clear cut.
They can, however, be made at the end of a quarter, a month, or even at the end of a day, depending on the accounting procedures and the nature of business carried on by the company. An adjusting entry for depreciation on fixed assets used to match use of a long term asset to revenue. A real account has a balance that is measured cumulatively, rather than from period to period. Salaries Expense increases (debit) and Salaries Payableincreases (credit) for $12,500 ($2,500 per employee × fiveemployees). The following are the updated ledger balances afterposting the adjusting entry. Income Tax Expense increases (debit) and Income Tax Payableincreases (credit) for $9,000.
There are various types of accounting adjusting entries examples in accounting a few of which are given below. Accumulated Depreciation is contrary to an asset account, suchas Equipment. This means that the normal balance for AccumulatedDepreciation is on the credit side. Accumulated Depreciationwill reduce the asset account for depreciation incurred up to thatpoint.
The revenue recognition principle requires businesses to recognize revenue when it is earned, regardless of when payment is received. Adjustment entries are necessary to ensure that revenue is recognized in the correct period, even if payment has not been received. For example, what is the difference between a sales return and a sales allowance if a company has received payment for services that it has not yet provided, an adjustment entry is needed to record the revenue earned but not yet received. Understanding adjustment entries is critical for anyone involved in accounting, finance, or business operations.
It updates previously recorded journal entries so that the financial statements at the end of the year are accurate and up-to-date. When you make an adjusting entry, you’re making sure the activities of your business are recorded accurately in time. If you don’t make adjusting entries, your books will show you paying for expenses before they’re actually incurred, or collecting unearned revenue before you can actually use the money. The entry records any unrecognized income or expenses for the accounting period, such as when a transaction starts in one accounting period and ends in a later period. Adjusting entries are accounting journal entries that are to be made at the end of an accounting period. Adjusting entries are sometimes referred to as balance day adjustments.

 English
English